2023.08.14
Technical progress of refractory materials for steel converter
Page view:340
Converter is an important equipment for steelmaking, it is a kind of steelmaking furnace which does not need external heat source and mainly uses hot pig iron, scrap steel and ferroalloy as raw materials. According to the properties of lining refractories, it is divided into acid converter and basic converter, and according to the parts of gas blown into the furnace, it is divided into bottom-blown converter, top-blown converter, side-blown converter and top-bottom combined blowing converter.
The converter steelmaking method has a long history, as early as 1856, the British Bessemer invented the bottom-blown acid converter, which was the beginning of modern steelmaking method. In 1879, the Thomas basic converter appeared, which could handle high phosphorus pig iron. In 1864, the French Martin used the principle of heat storage to create the open furnace steelmaking method, which once became the world's main steelmaking equipment, and in the 1950s, about 85% of the world's crude steel was smelted by the open furnace. In 1952, Austria appeared pure oxygen top-blown converter, which solved the problem of the content of nitrogen and other harmful impurities in steel, while reducing the heat lost with the waste gas, can blow pig iron with lower temperature, save the coke consumption of blast furnace, and can use more scrap steel, steel making speed is particularly fast (a furnace steel about 10 min, In 1968, oxygen bottom blowing method converter appeared, and in 1970, the bottom blowing method of double casing bottom blowing oxygen gun protected by hydrocarbons was invented, and various types of bottom blowing method (such as OBM, Q-BOP, LSW, etc.) showed many advantages over top blowing in actual production. The Austrians studied the top-bottom reblowing steelmaking process in 1973, and put it into production in the early 1980s, which is superior to the top-blowing and bottom-blowing, and some basically eliminated the pure top-blowing converter.
In China, in 1951, Tangshan Steel plant air side blown converter steelmaking test success, put into operation in 1952, 1954 began small oxygen top blown converter test success, 1962 Shougang air side blown converter into 3 t oxygen top blown converter, 1964 put into operation two 30 t top blown oxygen converter. With the steel mills in Tangshan, Shanghai, Hangzhou and other places have rebuilt 3.5-5 t top-blown oxygen converter, and then some large steel enterprises, such as Angang and Wuhan Iron and Steel, will change the open-hearth furnace to 250 ~ 300 t oxygen top-blown converter, put into production in 1985, Baosteel with advanced technology is also using 300 t large-scale oxygen top-blown converter steelmaking, since then, China has basically eliminated open-hearth steelmaking. In recent years, the emergence of top and bottom blowing composite blowing converter, sliding plate slag shield technology, so that the smelting time is shortened, the composition and temperature of molten steel is more uniform, reduce the inclusions in steel, improve the cleanliness of molten steel and other advantages, some steel mills in China also generally adopt the top and bottom composite blowing technology. According to statistics, converter steel accounts for more than 70% of the world's total crude steel production, while China accounts for 90%.
The converter is basically made of refractory materials, and the cost of refractory materials for steelmaking accounts for about 9% to 13% of the cost of the steelmaking process. Due to the different composition of hot metal and refractory raw material resources in various countries, the choice of furnace lining refractory materials also has its own focus, Europe, the United States, Russia and other industrial developed has developed from dolomite, magnesium products to the present magnesia carbon brick, Japan is the first to use magnesia carbon brick. China's converter lining through tar dolomite, tar magnesia, magnesia dolomite, magnesia dolomite carbon brick to now widely used magnesia carbon brick. Due to the corrosion resistance, thermal shock resistance, wear resistance, good thermal conductivity, anti-spalling, stable performance at high temperature, the converter lining is widely used in various countries. The performance and quality of refractory materials directly affect the steel making method and service life of the converter, which is of great significance to improve product quality and economic benefits. The problem of refractory materials used in the converter has aroused people's attention, and some new technologies of refractory materials have emerged, such as spray repair technology, slag splashing furnace protection technology, sliding water nozzle slag blocking technology.
Furnace age is an important technical index of converter steelmaking. Increasing the furnace life not only reduces the production cost, but also improves the production efficiency. In recent years, through the development and research of scientific and technical personnel, the life of the lining has been significantly improved, and the single consumption of refractory material has been reduced to 2 ~ 0.38 kg/t steel. Specific measures are as follows.
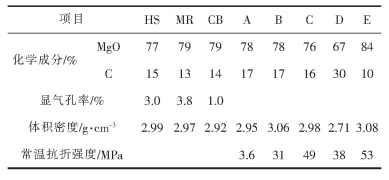
表1 系列镁碳砖的性能
Previous:Erosion mechanism and developm...
Next:Application technology and dev...
